Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Tuft cells have recently emerged as the focus of intense interest following the discovery of their chemosensory role in the intestinal tract, and their ability to activate Type 2 immune responses to helminth parasites. Moreover, they populate a wide range of mucosal tissues and are intimately connected to immune and neuronal cells, either directly or through the release of pharmacologically active mediators. They are now recognised to fulfil both homeostatic roles, in metabolism and tissue integrity, as well as acting as the first sensors of parasite infection, immunity to which is lost in their absence. In this review we focus primarily on the importance of tuft cells in the intestinal niche, but also link to their more generalised physiological role and discuss their potential as targets for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders.
Cancers, Free Full-Text

Sequencing of Circulating Cell-free DNA during Pregnancy
Cells, Free Full-Text
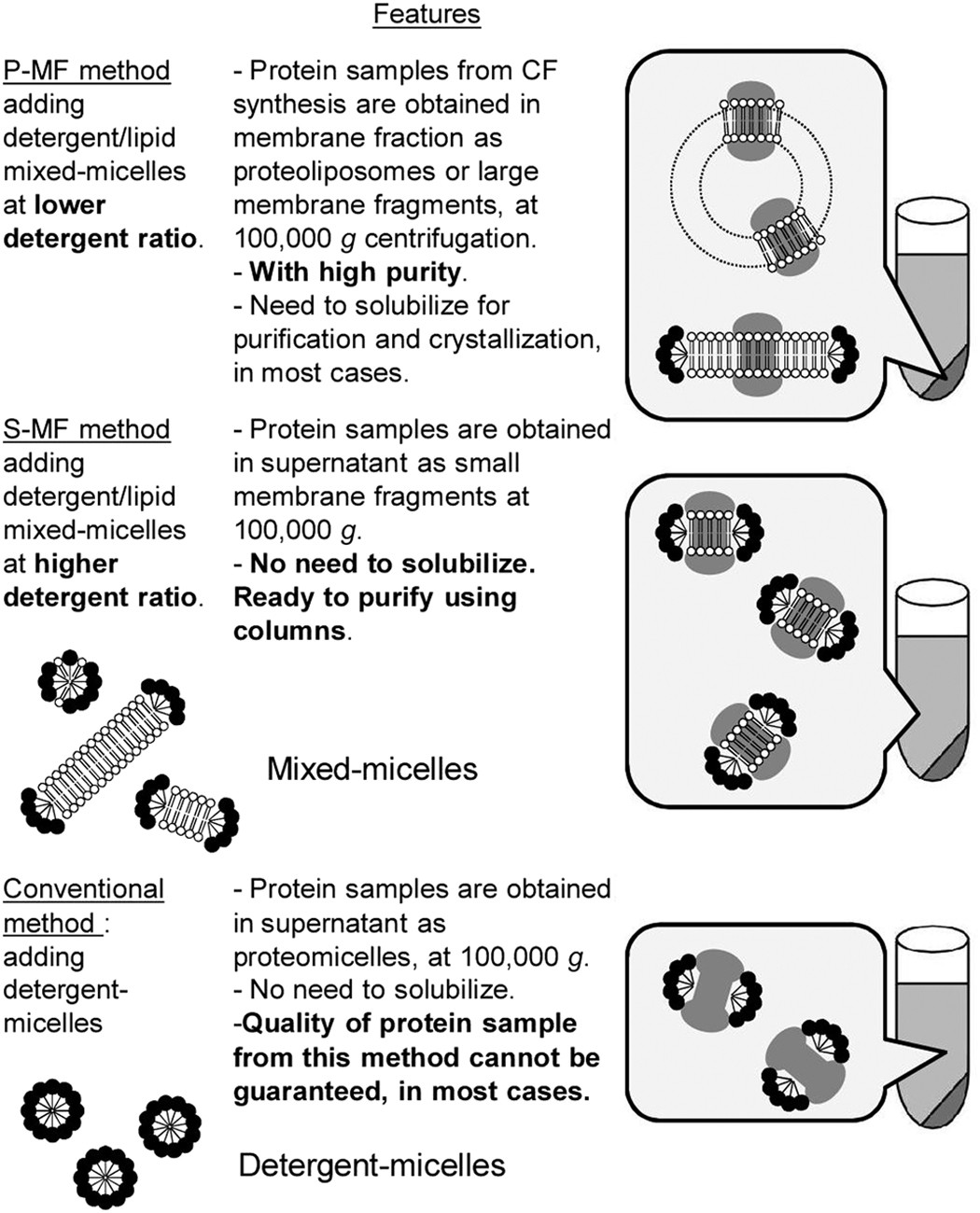
Cell-free methods to produce structurally intact mammalian membrane proteins

PDF] Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as New Remedy for the Treatment of Neurocognitive Disorders
IAPP/amylin-induced interaction between NLRP3 and ASC in a cell-free
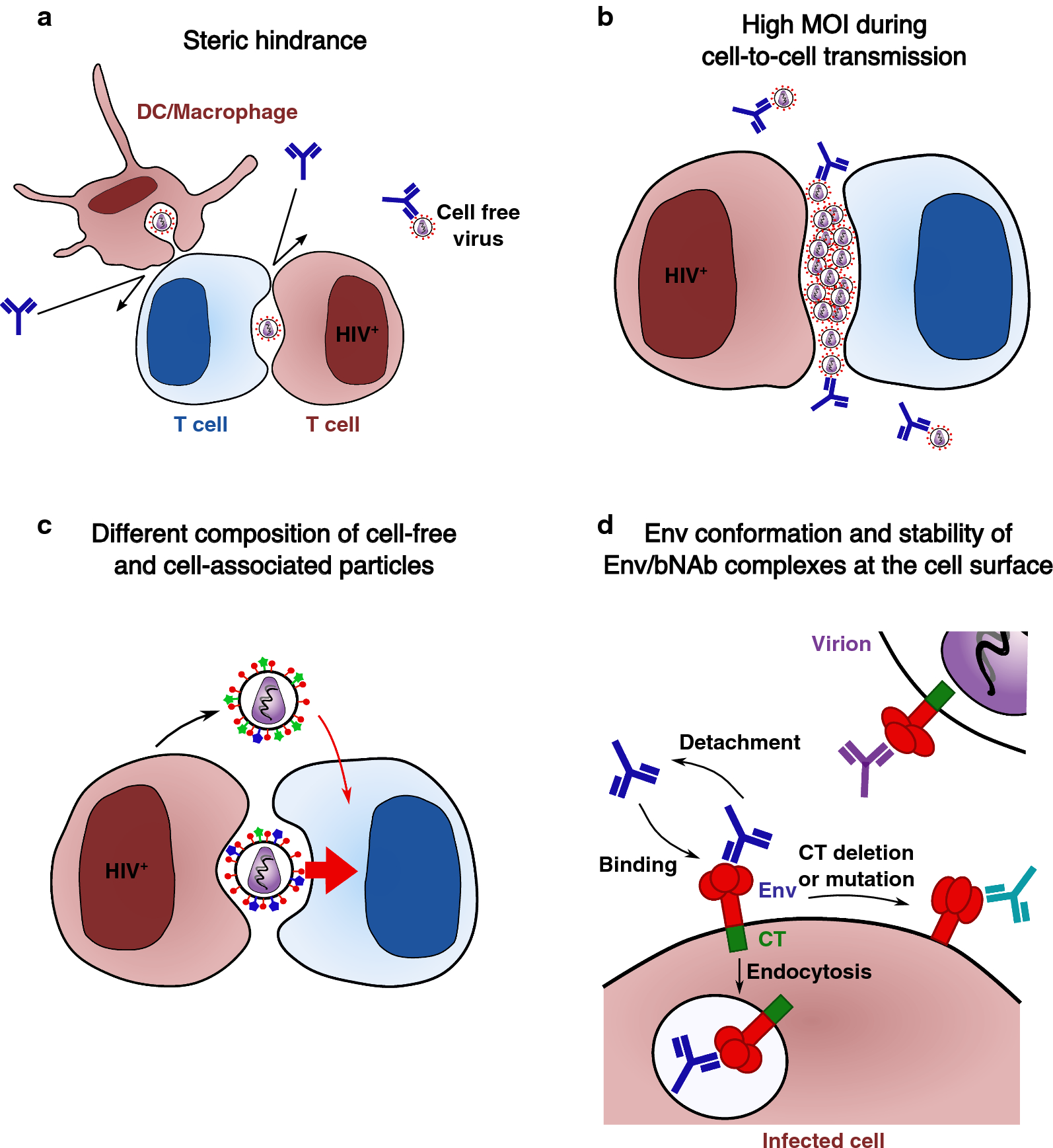
HIV-1 cell-to-cell transmission and broadly neutralizing antibodies, Retrovirology

Nucleic acid biomarkers of immune response and cell and tissue damage in children with COVID-19 and MIS-C - ScienceDirect
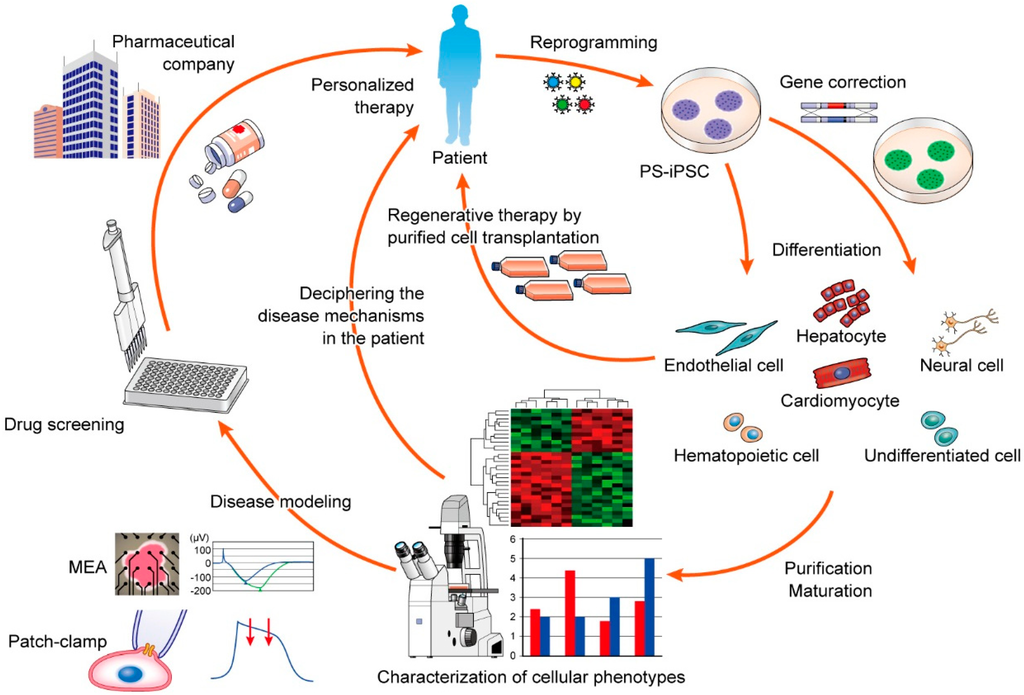
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Circulating Tumor Cells, Disease Progression, and Survival in Metastatic Breast Cancer
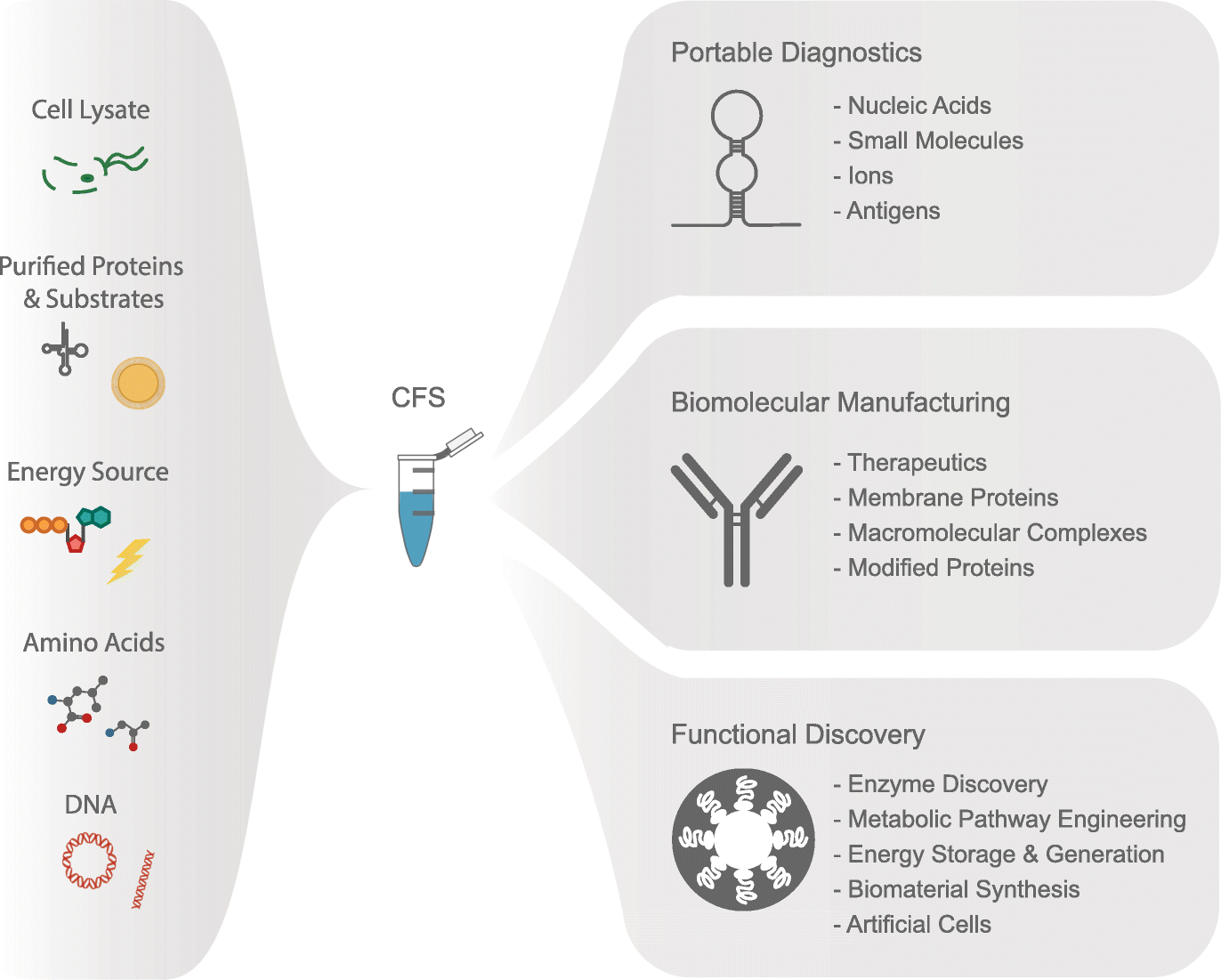
Cells, Free Full-Text
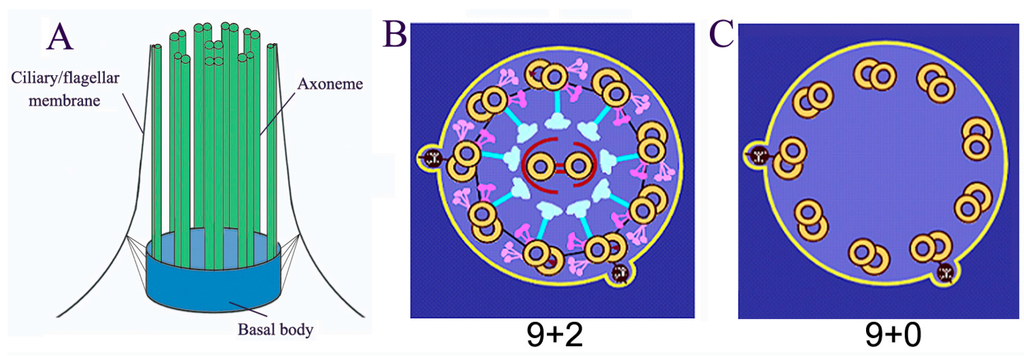
Cells, Free Full-Text
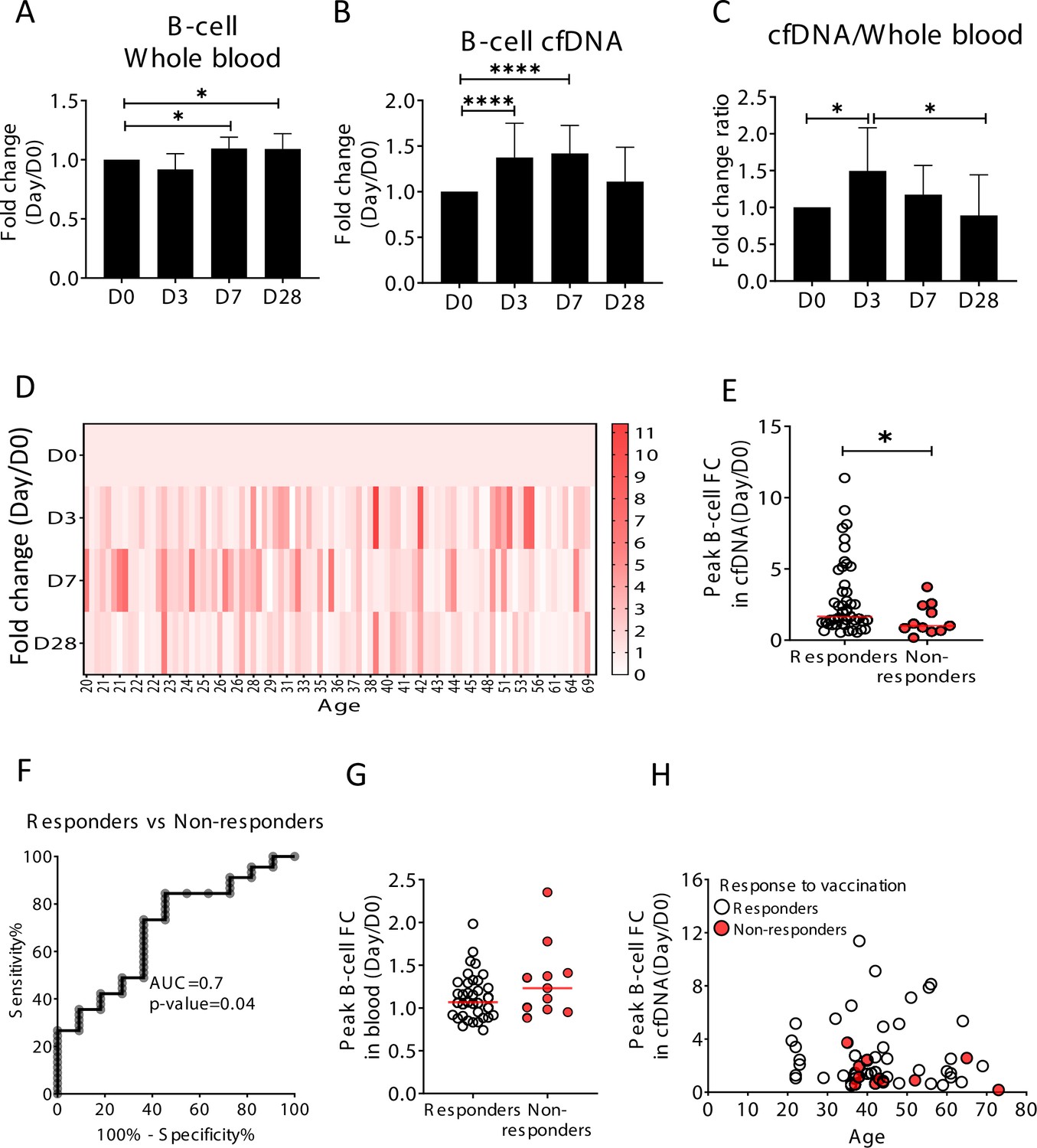
Remote immune processes revealed by immune-derived circulating cell-free DNA
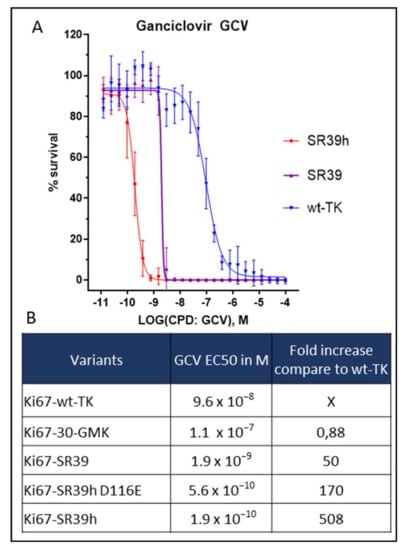
Serial Number Alcohol 120 1.9 6 - Colaboratory
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)