Hydrology, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Estimating intensity−duration−frequency (IDF) curves requires local historical information of precipitation intensity. When such information is unavailable, as in areas without rain gauges, it is necessary to consider other methods to estimate curve parameters. In this study, three methods were explored to estimate IDF curves in ungauged areas: Kriging (KG), Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW), and Storm Index (SI). To test the viability of these methods, historical data collected from 31 rain gauges distributed in central Chile, 35° S to 38° S, are used. As a result of the reduced number of rain gauges to evaluate the performance of each method, we used LOOCV (Leaving One Out Cross Validation). The results indicate that KG was limited due to the sparse distribution of rain gauges in central Chile. SI (a linear scaling method) showed the smallest prediction error in all of the ungauged locations, and outperformed both KG and IDW. However, the SI method does not provide estimates of uncertainty, as is possible with KG. The simplicity of SI renders it a viable method for extrapolating IDF curves to locations without data in the central zone of Chile.

Hydrology: Problems, Challenges and Opportunities

Hydrologic Cycle and Interactions

Hydrology and floodplain analysis 5th edition bedient solutions

SOLUTION: Applied hydrology ven te chow - Studypool
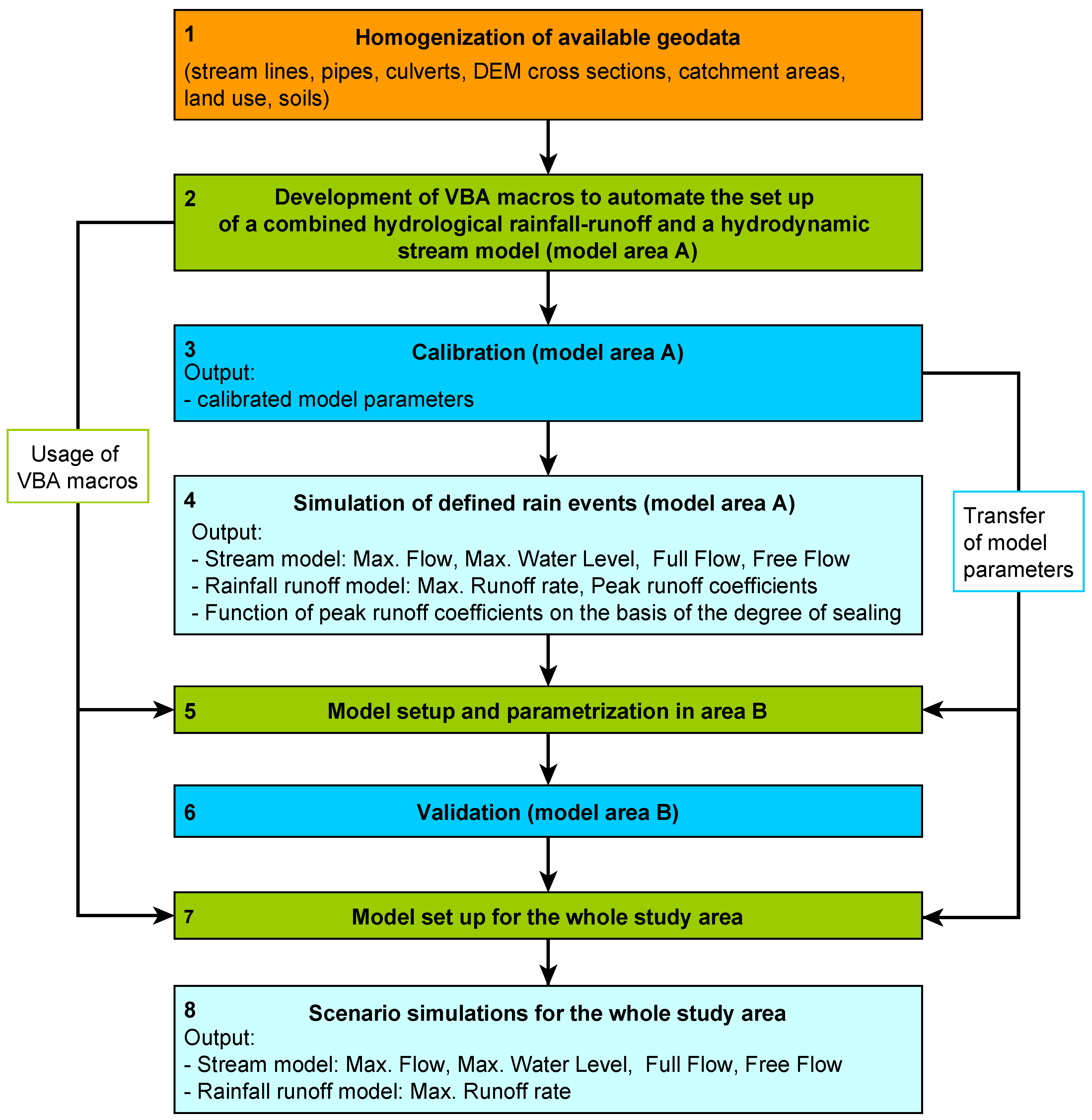
Hydrology, Free Full-Text
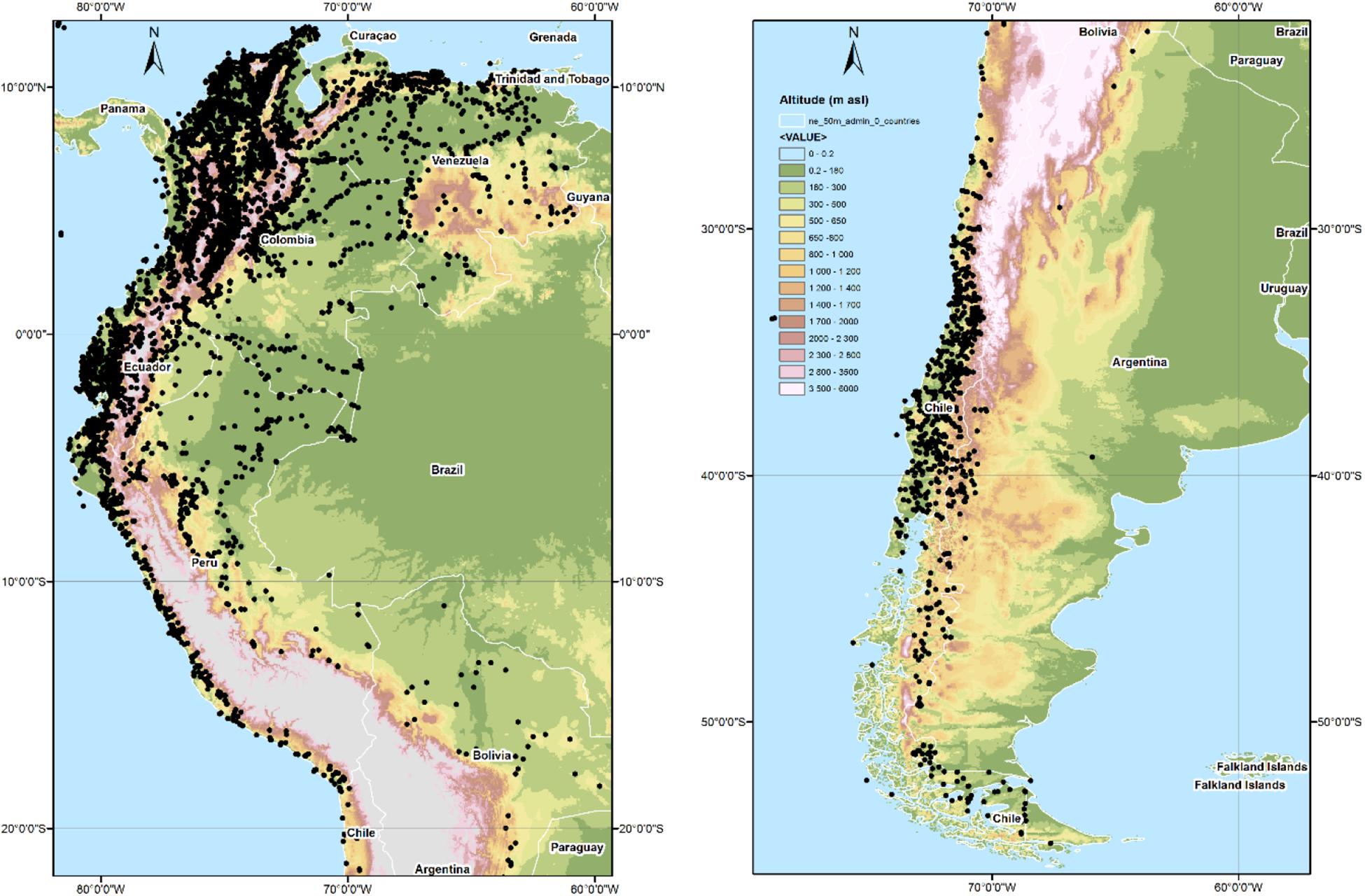
Frontiers Climatological and Hydrological Observations for the
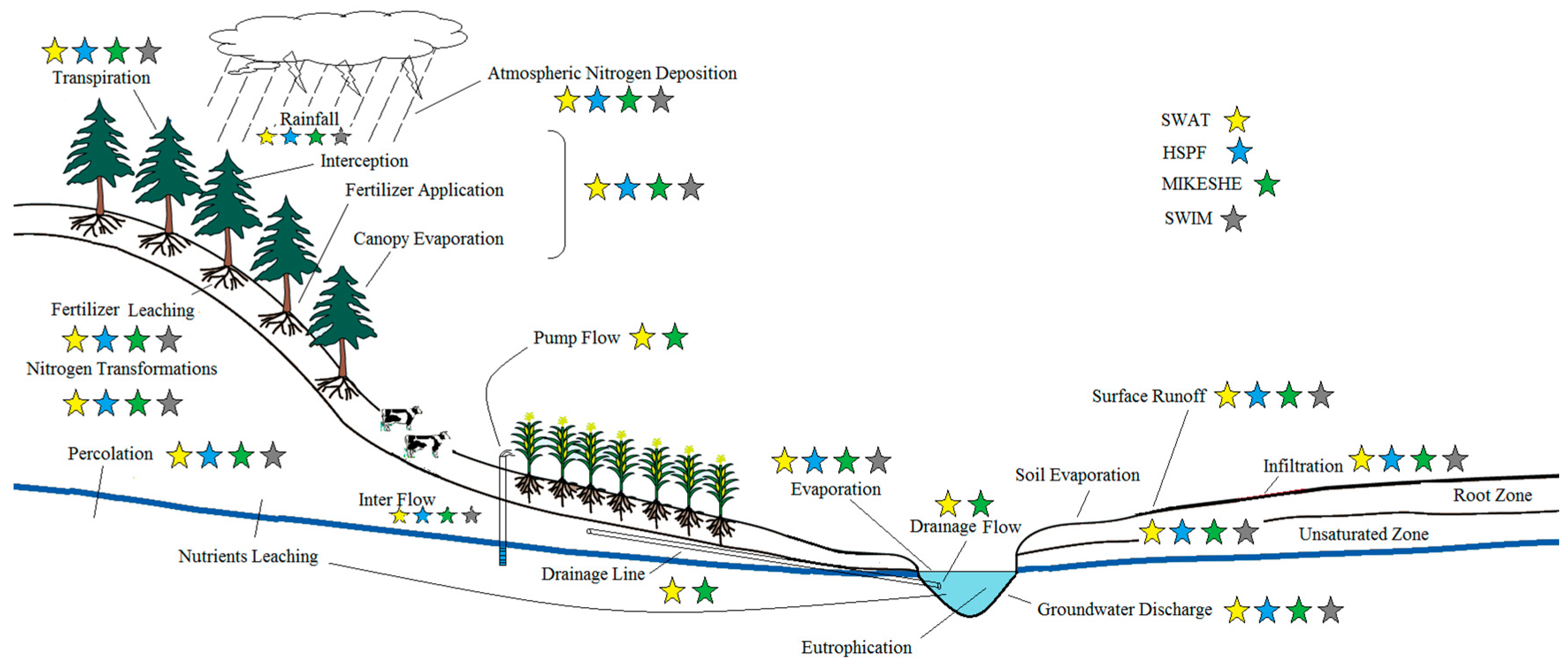
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text

Southeastern Naturalist, Volume 12, Monograph Number 5 (2013): 1–36
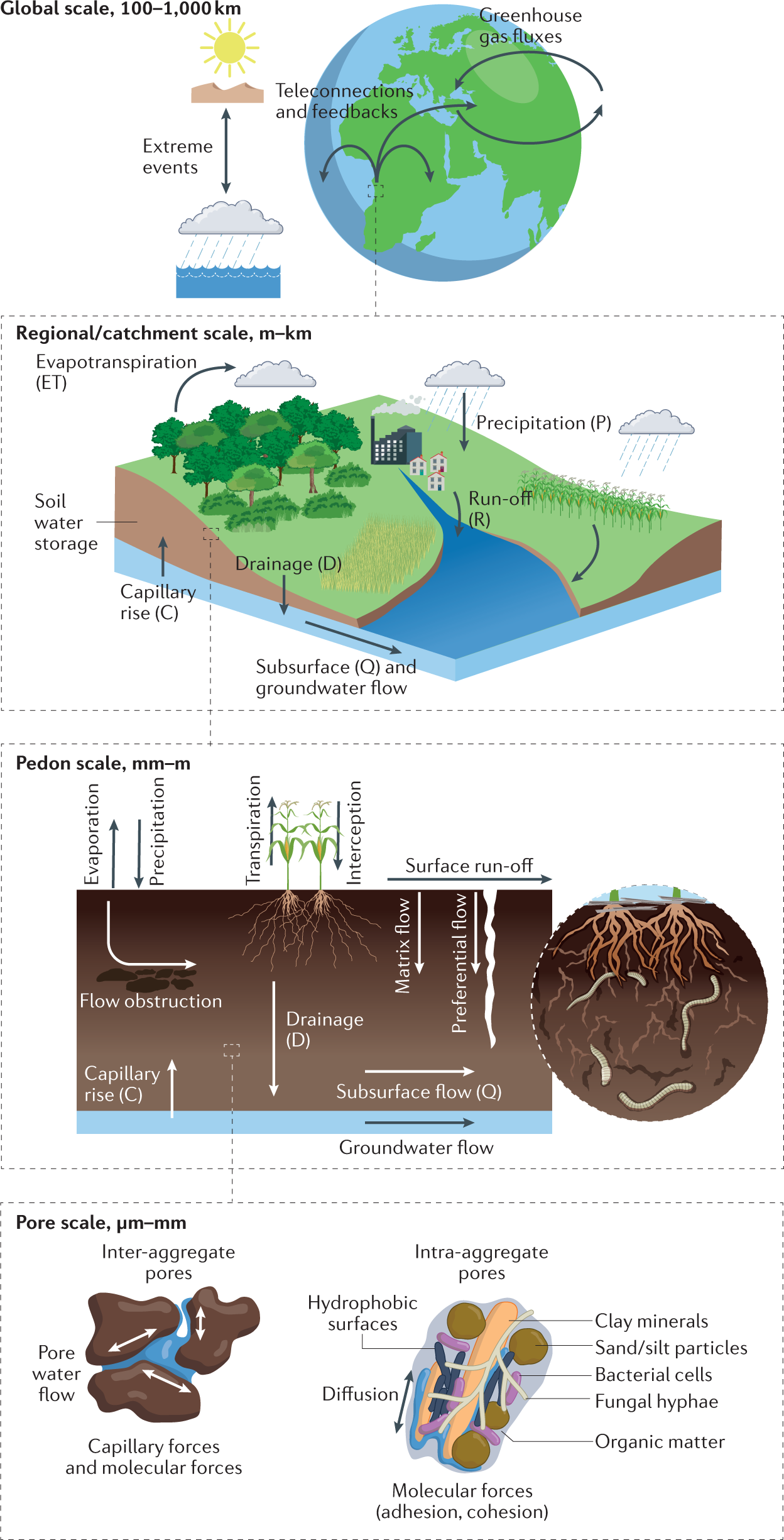
Soil hydrology in the Earth system

Hydrology for Engineers (McGraw-Hill by Linsley, Ray K.
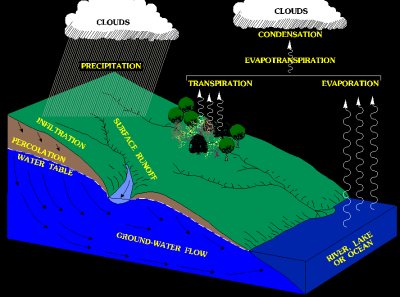
Simplified hydrologic cycle

Daniel González-Fernández on X: We are hiring a POSTDOC with
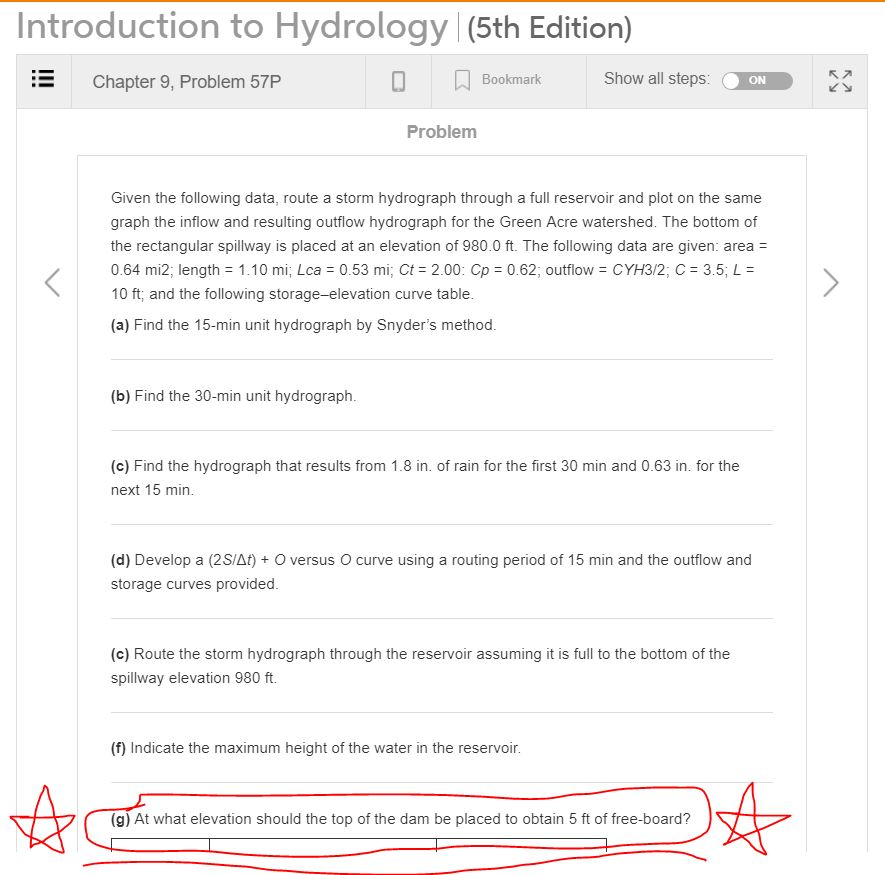
Introduction to Hydrology (5th Edition) Chapter 9
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)






