J. Compos. Sci., Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Spider silk is an astonishingly tough biomaterial that consists almost entirely of large proteins. Studying the secrets behind the high strength nature of spider webs is very challenging due to their miniature size. In spite of their complex nature, researchers have always been inspired to mimic Nature for developing new products or enhancing the performance of existing technologies. Accordingly, the spider web can be taken as a model for optimal fiber orientation for composite materials to be used in critical structural applications. In this study an attempt is made to analyze the geometrical characteristics of the web construction building units such as spirals and radials. As a measurement tool, we have used a developed MATLAB algorithm code for measuring the node to node of rings and radials angle of orientation. Spider web image samples were collected randomly from an ecological niche with black background sample collection tools. The study shows that the radial angle of orientation is 12.7 degrees with 5 mm distance for the spirals’ mesh size. The extracted geometrical numeric values from the spider web show moderately skewed statistical data. The study sheds light on spider web utilization to develop an optimized fiber orientation reinforced composite structure for constructing, for instance, shell structures, pressure vessels and fuselage cones for the aviation industry.

Multifunctional Carbon Fiber Composites: A Structural, Energy Harvesting, Strain-Sensing Material
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text

The drivers and impacts of forest degradation

Full article: Recent advancements in conducting polymer bionanocomposites and hydrogels for biomedical applications
Sustainability, Free Full-Text
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text
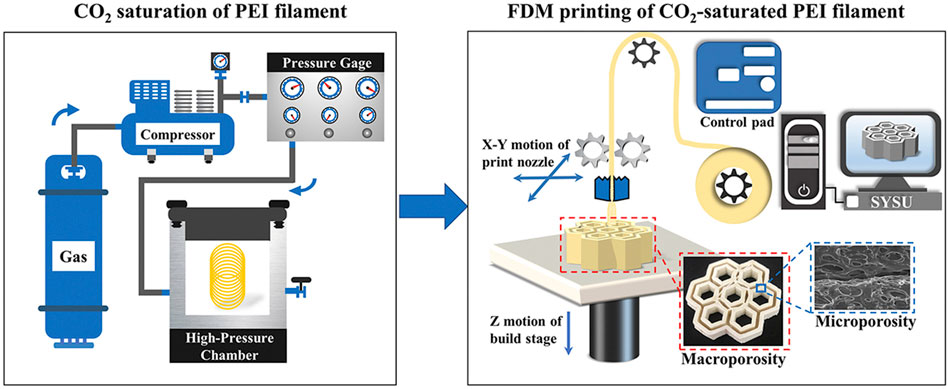
Frontiers Research progress of 3D printing combined with thermoplastic foaming

Dual-Mode and Label-Free Detection of Exosomes from Plasma Using an Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring

Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 - The Lancet
Journal of Composites Science An Open Access Journal from MDPI
JMSE, Free Full-Text
J. Compos. Sci., Free Full-Text

Catalyst-free self-healing bio-based vitrimer for a recyclable, reprocessable, and self-adhered carbon fiber reinforced composite - ScienceDirect
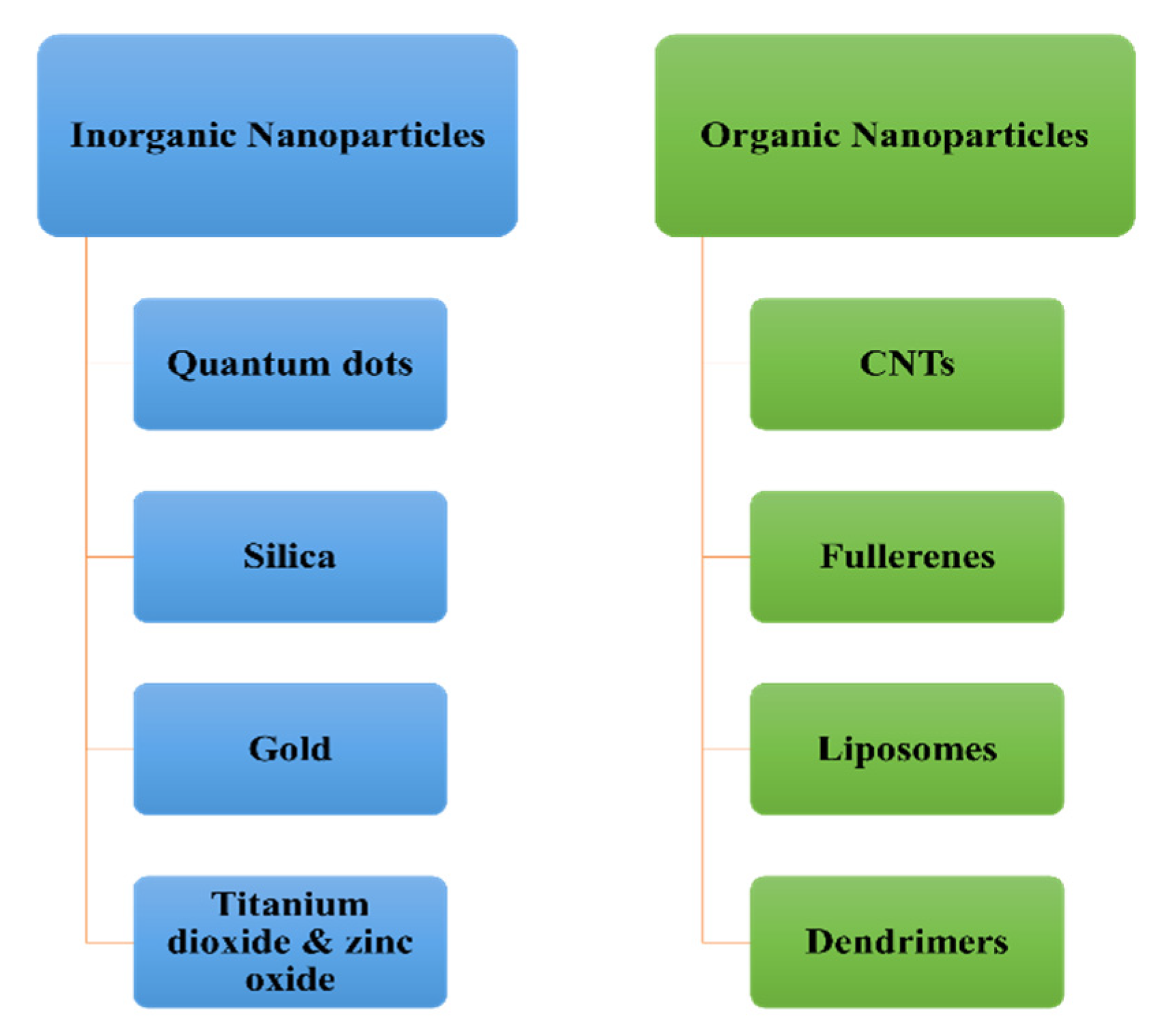
J. Compos. Sci., Free Full-Text
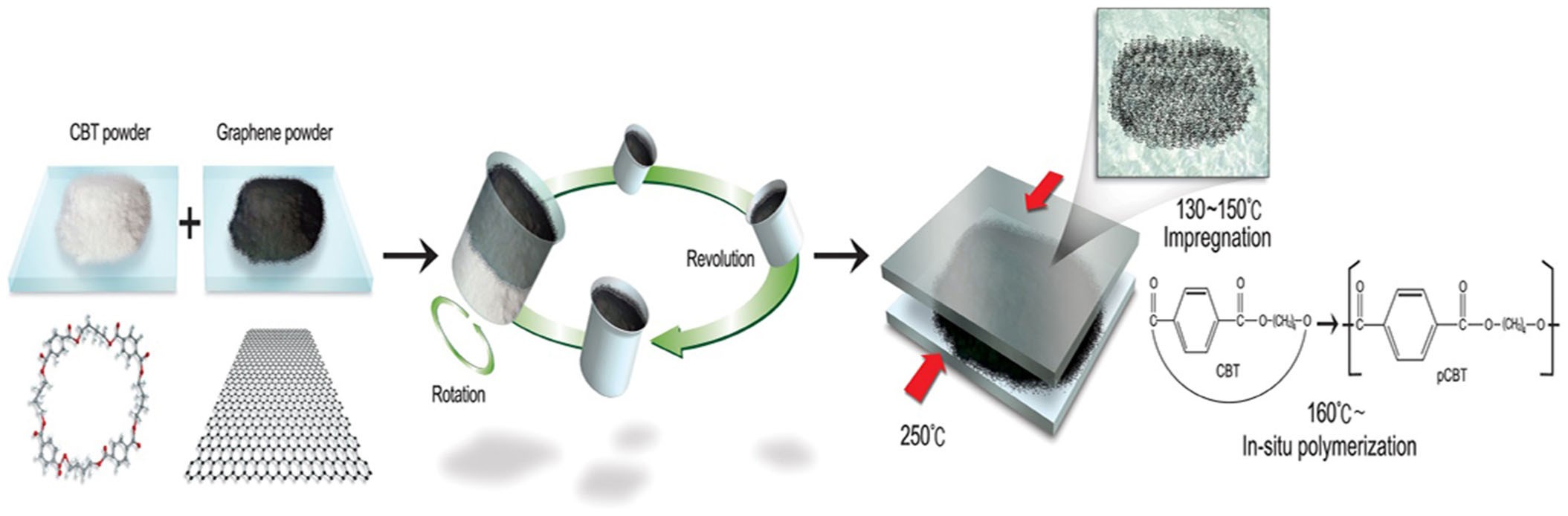
Ultra-high dispersion of graphene in polymer composite via solvent freefabrication and functionalization
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)

/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/XAZDQDPV3VJRVJH2CCQBJRJ7EI.jpg)