Staphylococcus Aureus Cells, Heat-Inactivated
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
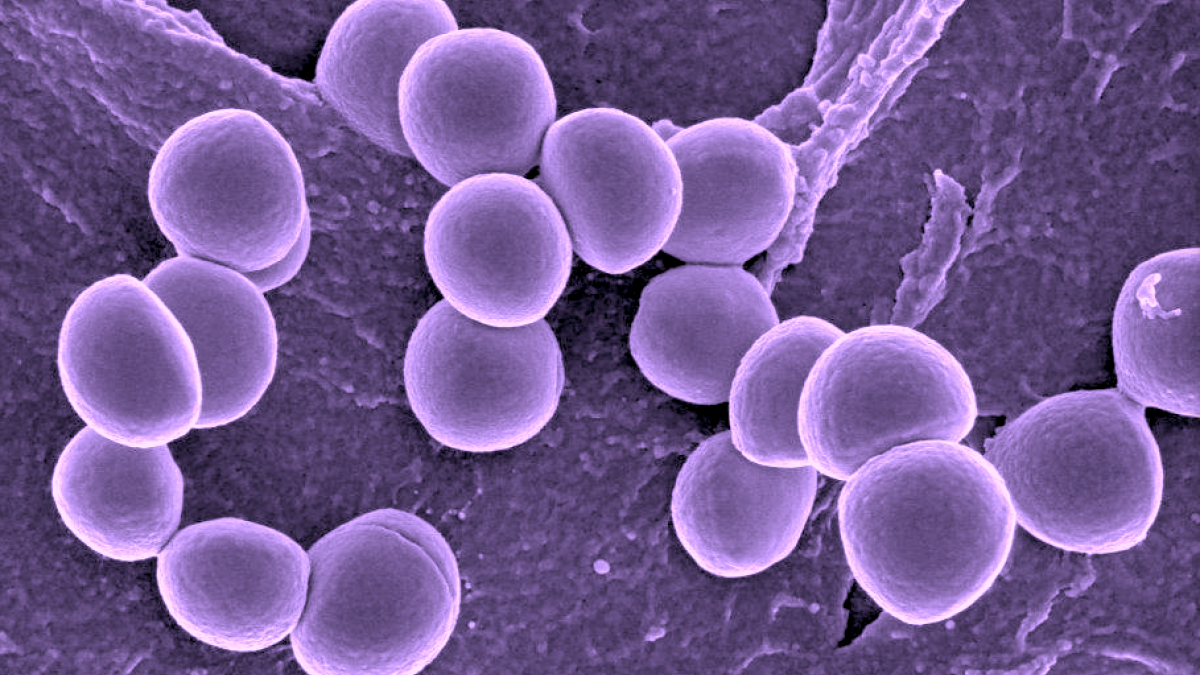
Heat-killed Staphylococcus aureus cells in dextran solution. Antigen is intended for use as a positive control in immunoassay development for

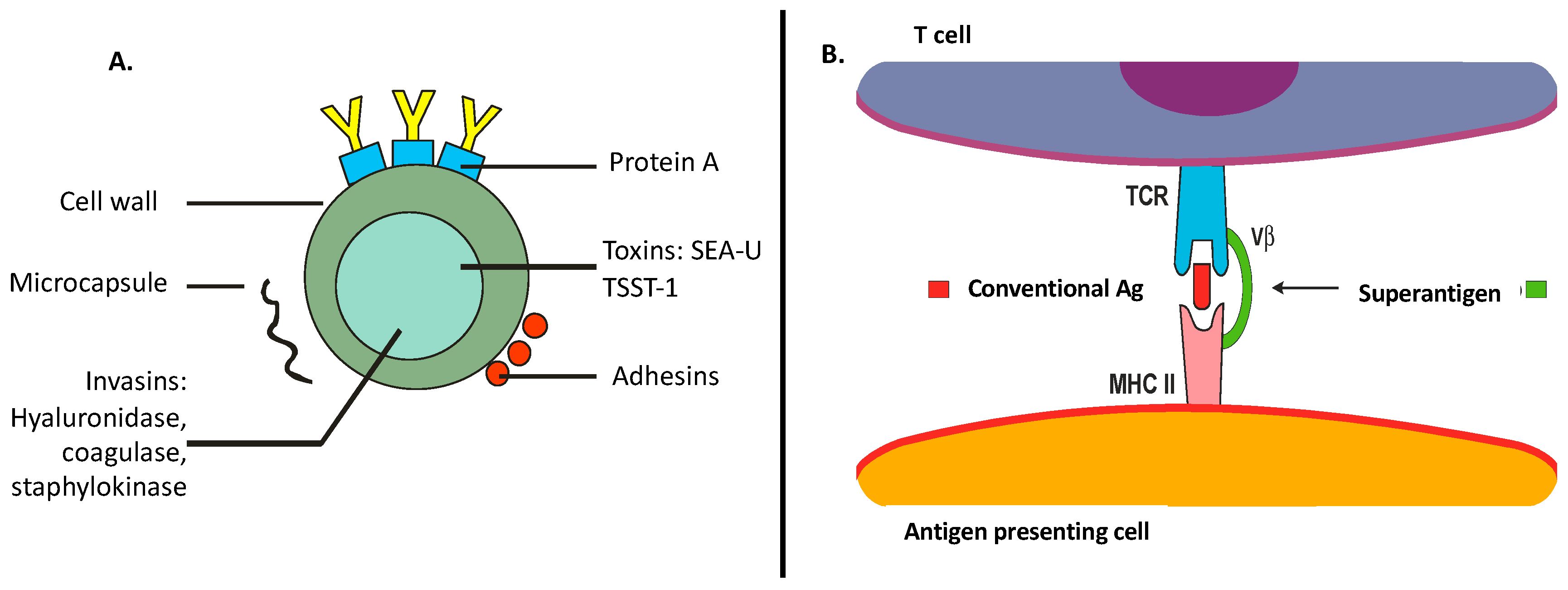
Determinants of Staphylococcus aureus Colonization and Infection.“Exploring the Role of Cell Wall Anchored Proteins in Adhesion and Immune Evasion”

N6-Methyladenosine Modification Profile in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells Treated with Heat-Inactivated Staphylococcus aureus

Drug-Repurposing Approach To Combat Staphylococcus aureus: Biomolecular and Binding Interaction Study
Commensal bacteria augment Staphylococcus aureus infection by inactivation of phagocyte-derived reactive oxygen species

Growth curve of Staphylococcus aureus.
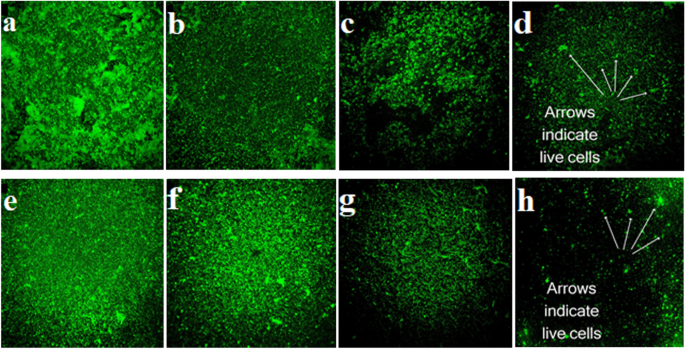
Inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli Biofilms by Air-Based Atmospheric-Pressure DBD Plasma
Heat-killed Staphylococcus aureus cells in dextran solution. Antigen is intended for use as a positive control in immunoassay development for
Staphylococcus Aureus Cells, Heat-Inactivated
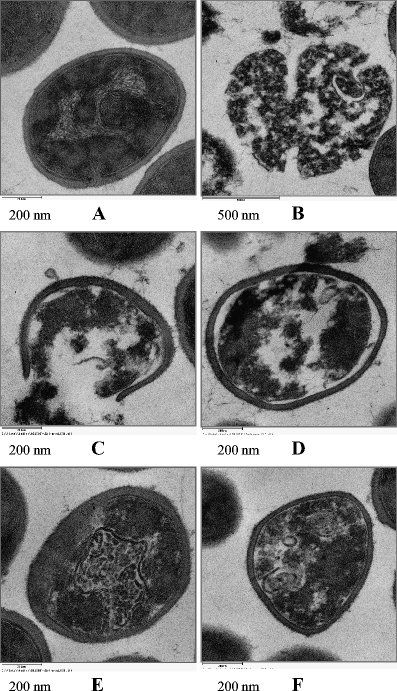
Microscopic and Spectroscopic Evaluation of Inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus by Pulsed UV Light and Infrared Heating
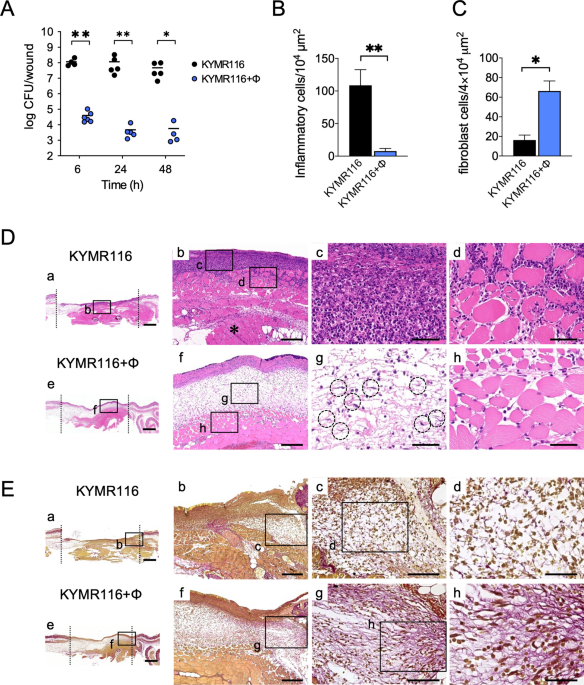
Modification of the immune response by bacteriophages alters methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection

SciELO - Brasil - Identification of key genes in bovine mammary epithelial cells challenged with Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus by integrated bioinformatics analysis Identification of key genes in bovine mammary epithelial
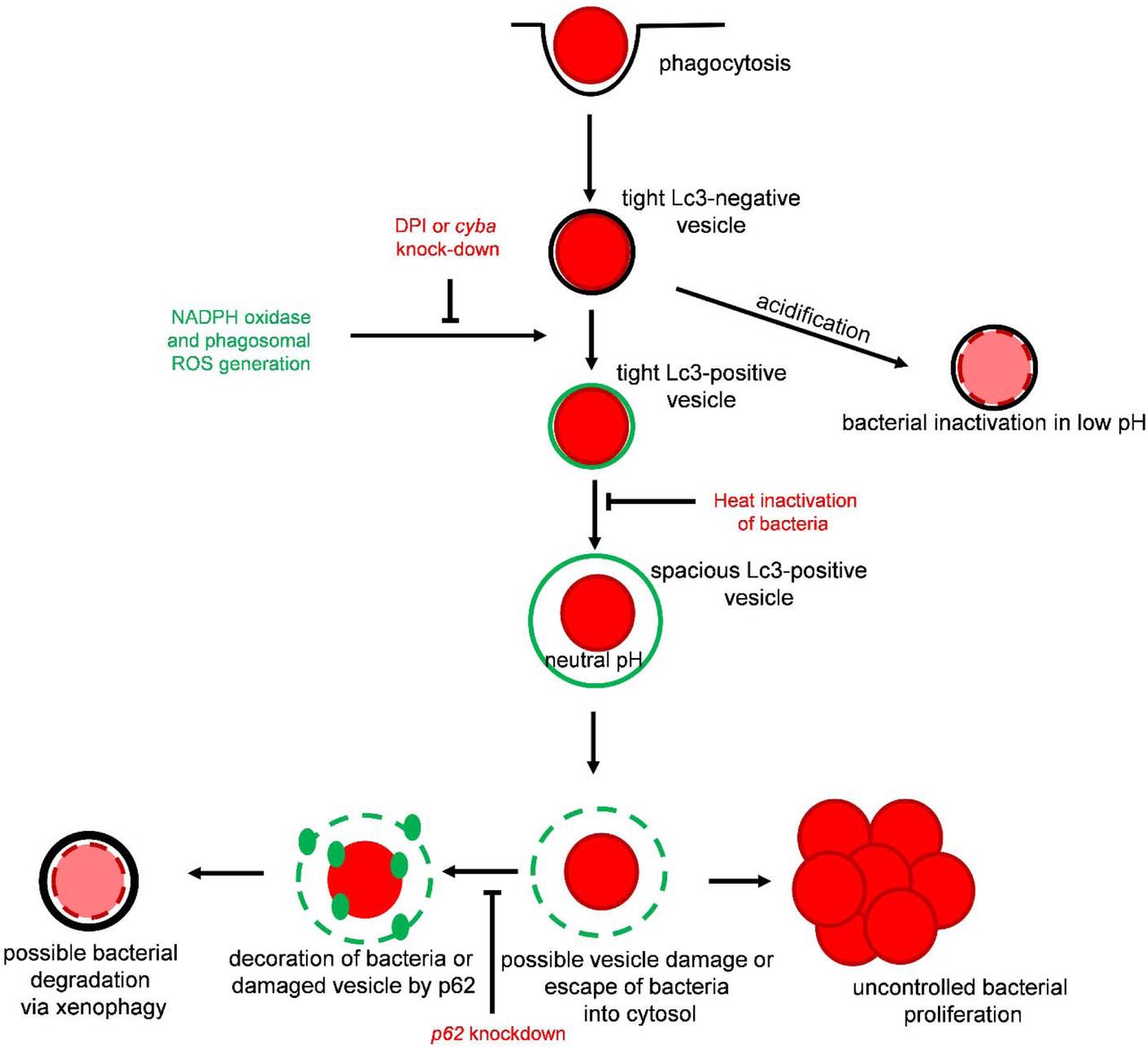
The autophagic response to Staphylococcus aureus provides an intracellular niche in neutrophils
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)