Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
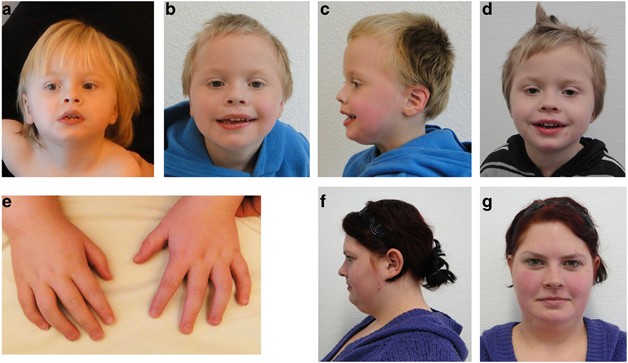
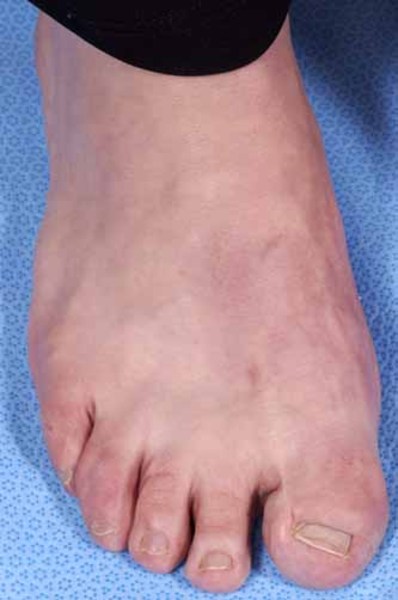
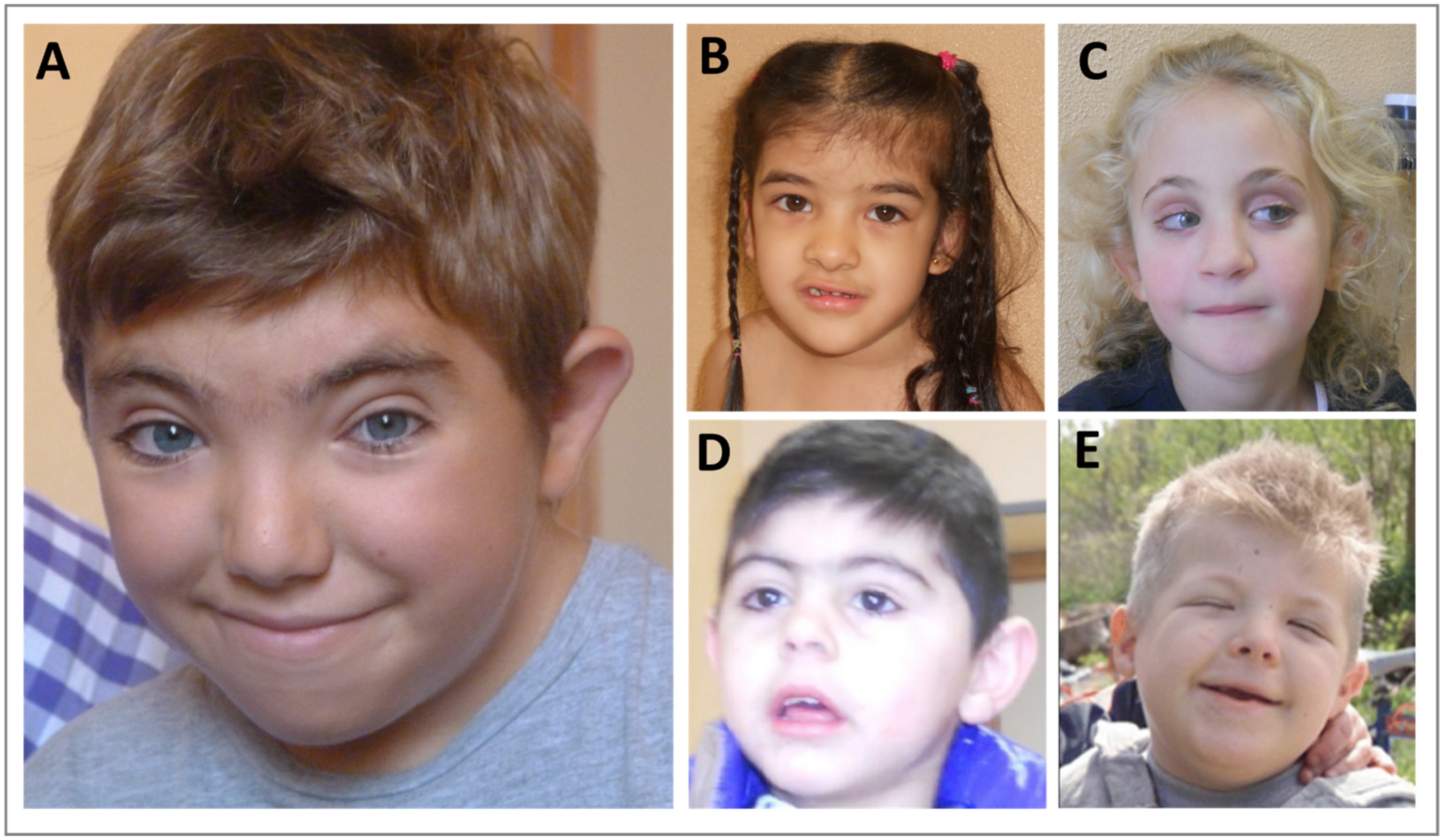
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RSTS) is characterized by distinctive facial features, broad and often angulated thumbs and halluces, short stature, and moderate-to-severe intellectual disability. Characteristic craniofacial features include downslanted palpebral fissures, low-hanging columella, high palate, grimacing smile, and talon cusps. Prenatal growth is often normal, then height, weight, and head circumference percentiles rapidly drop in the first few months of life. Short stature is typical in adulthood. Obesity may develop in childhood or adolescence. Average IQ ranges between 35 and 50; however, developmental outcome varies considerably. Some individuals with EP300-related RSTS have normal intellect. Additional features include ocular abnormalities, hearing loss, respiratory difficulties, congenital heart defects, renal abnormalities, cryptorchidism, feeding problems, recurrent infections, and severe constipation.
PDF) Approach to inherited hypertrichosis: A brief review
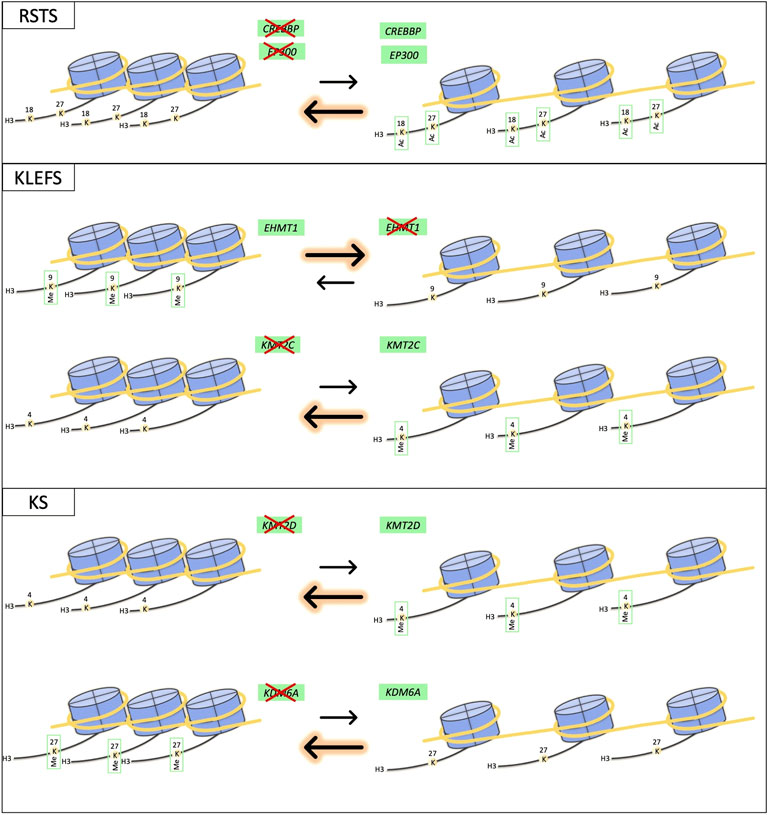
Frontiers Epigenetic disorders: Lessons from the animals–animal models in chromatinopathies
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: MedlinePlus Genetics

Genes, Free Full-Text

Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome - Wikipedia

genereviews.org - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf
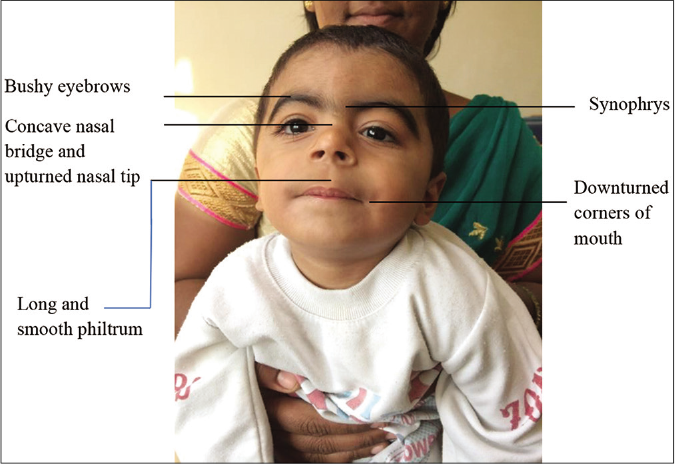
Approach to inherited hypertrichosis: A brief review - Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology

Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome 2 disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome 1
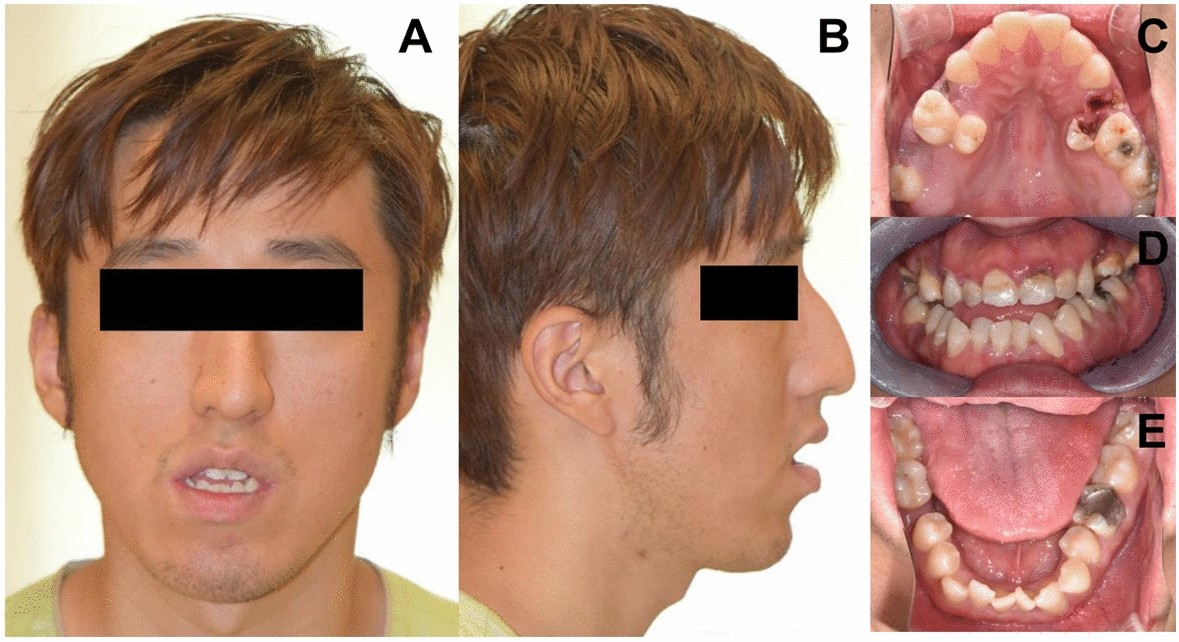
Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
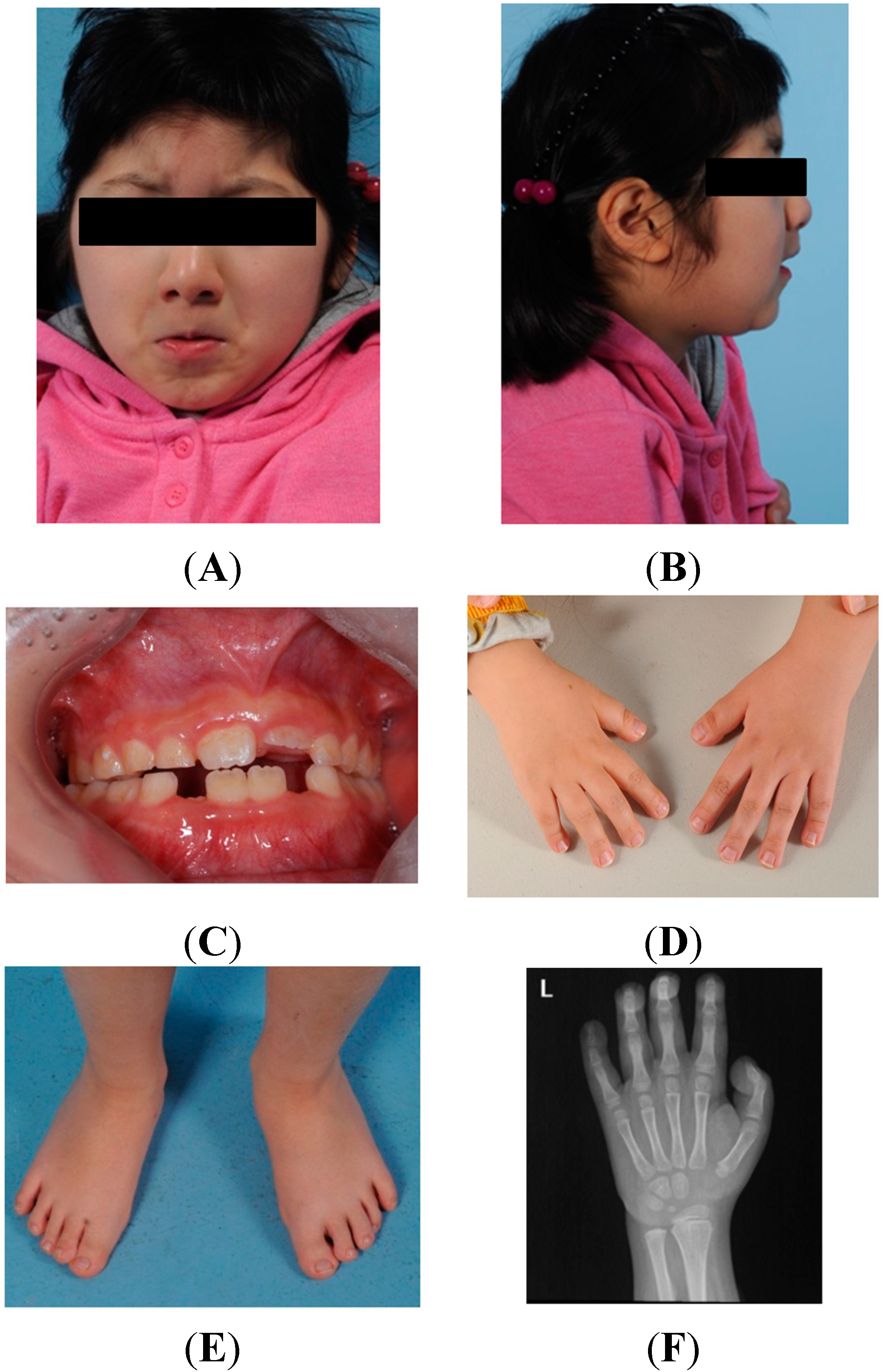
IJMS, Free Full-Text
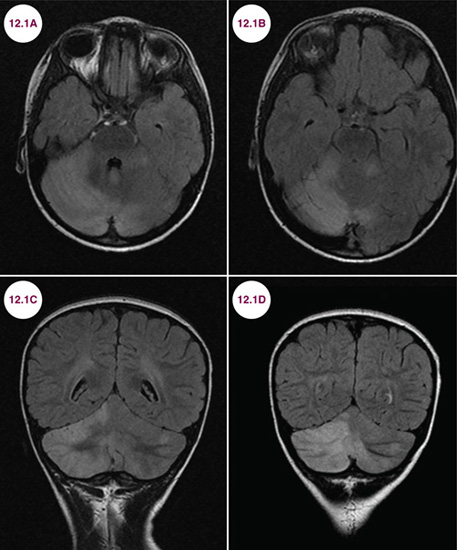
Pediatrics Neupsy Key
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)