Niemann-Pick disease type C, Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
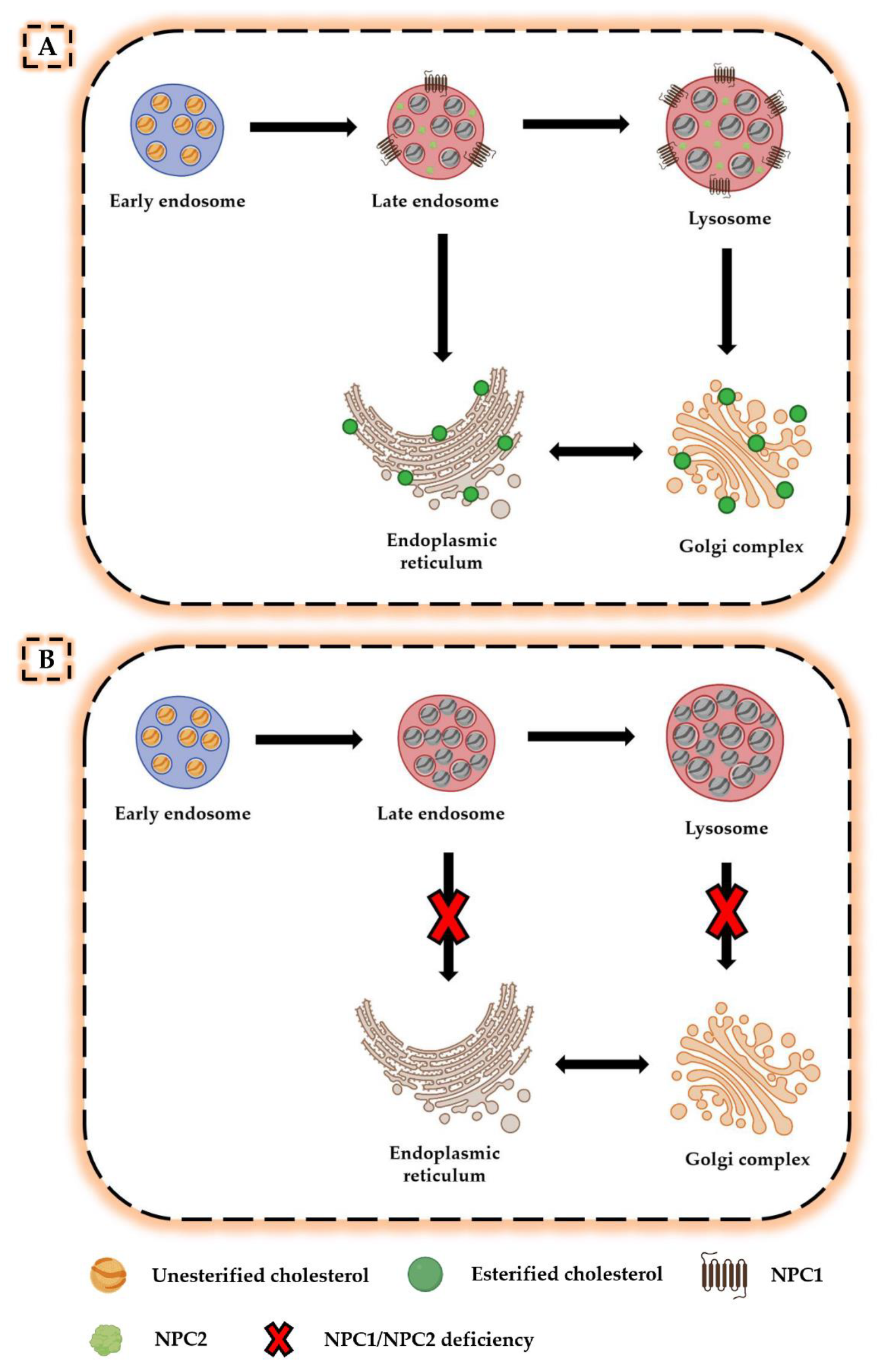
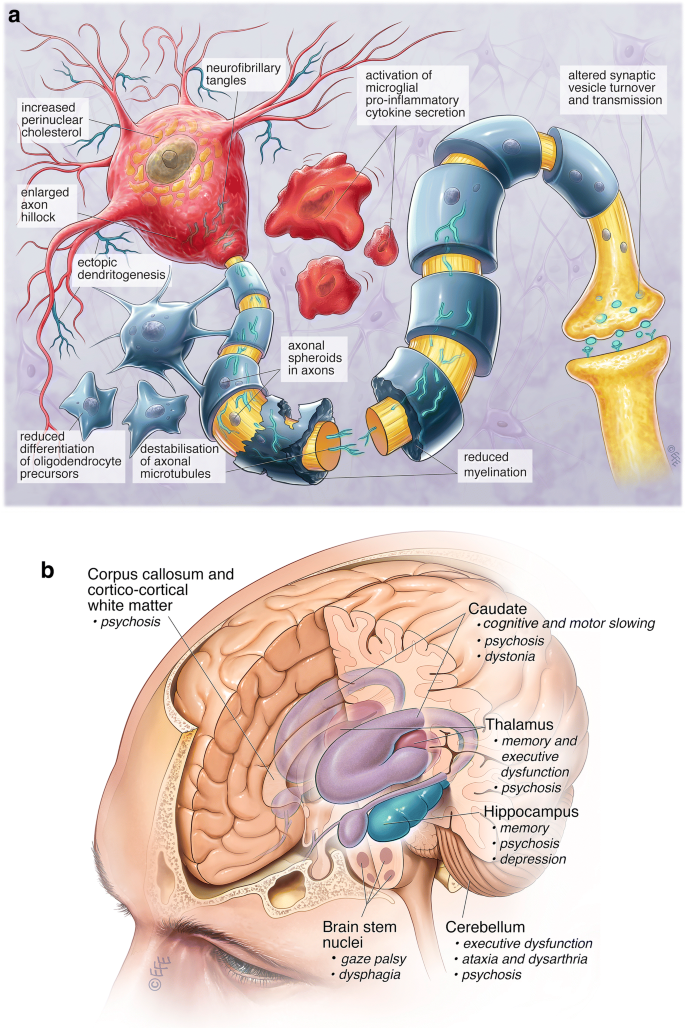
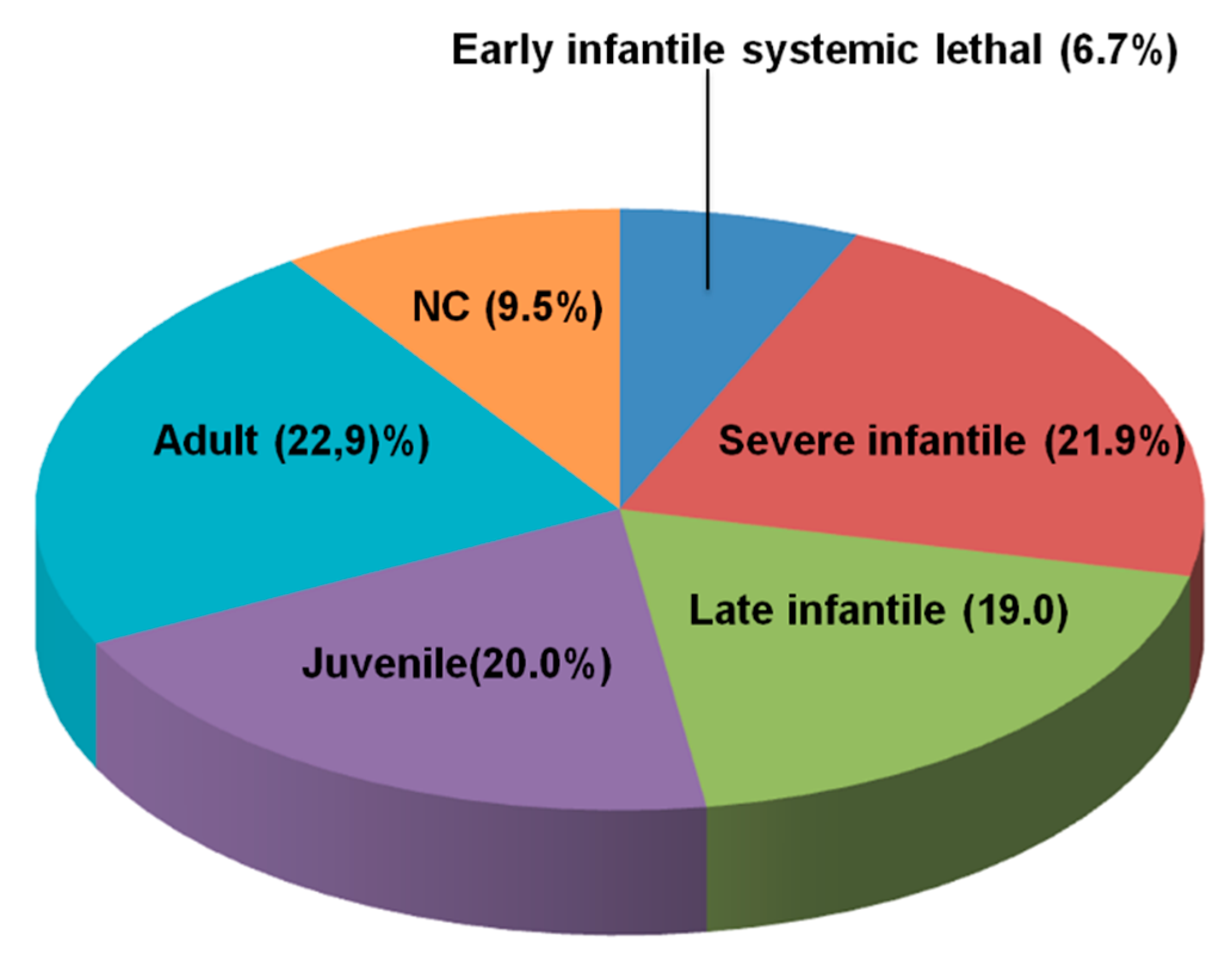
Niemann-Pick C disease (NP-C) is a neurovisceral atypical lysosomal lipid storage disorder with an estimated minimal incidence of 1/120 000 live births. The broad clinical spectrum ranges from a neonatal rapidly fatal disorder to an adult-onset chronic neurodegenerative disease. The neurological involvement defines the disease severity in most patients but is typically preceded by systemic signs (cholestatic jaundice in the neonatal period or isolated spleno- or hepatosplenomegaly in infancy or childhood). The first neurological symptoms vary with age of onset: delay in developmental motor milestones (early infantile period), gait problems, falls, clumsiness, cataplexy, school problems (late infantile and juvenile period), and ataxia not unfrequently following initial psychiatric disturbances (adult form). The most characteristic sign is vertical supranuclear gaze palsy. The neurological disorder consists mainly of cerebellar ataxia, dysarthria, dysphagia, and progressive dementia. Cataplexy, seizures and dystonia are other common features. NP-C is transmitted in an autosomal recessive manner and is caused by mutations of either the NPC1 (95% of families) or the NPC2 genes. The exact functions of the NPC1 and NPC2 proteins are still unclear. NP-C is currently described as a cellular cholesterol trafficking defect but in the brain, the prominently stored lipids are gangliosides. Clinical examination should include comprehensive neurological and ophthalmological evaluations. The primary laboratory diagnosis requires living skin fibroblasts to demonstrate accumulation of unesterified cholesterol in perinuclear vesicles (lysosomes) after staining with filipin. Pronounced abnormalities are observed in about 80% of the cases, mild to moderate alterations in the remainder ("variant" biochemical phenotype). Genotyping of patients is useful to confirm the diagnosis in the latter patients and essential for future prenatal diagnosis. The differential diagnosis may include other lipidoses; idiopathic neonatal hepatitis and other causes of cholestatic icterus should be considered in neonates, and conditions with cerebellar ataxia, dystonia, cataplexy and supranuclear gaze palsy in older children and adults. Symptomatic management of patients is crucial. A first product, miglustat, has been granted marketing authorization in Europe and several other countries for specific treatment of the neurological manifestations. The prognosis largely correlates with the age at onset of the neurological manifestations.

mRNA Treatment Rescues Niemann–Pick Disease Type C1 in Patient Fibroblasts

Adult‐onset Niemann–Pick disease type C masquerading as spinocerebellar ataxia - Vo - 2022 - Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine - Wiley Online Library

Laboratory diagnosis of Niemann–Pick disease type C: The filipin staining test - ScienceDirect
Niemann-Pick disease type C, Radiology Reference Article
JCM, Free Full-Text
Niemann-Pick Disease, Type C1 disease: Malacards - Research Articles, Drugs, Genes, Clinical Trials
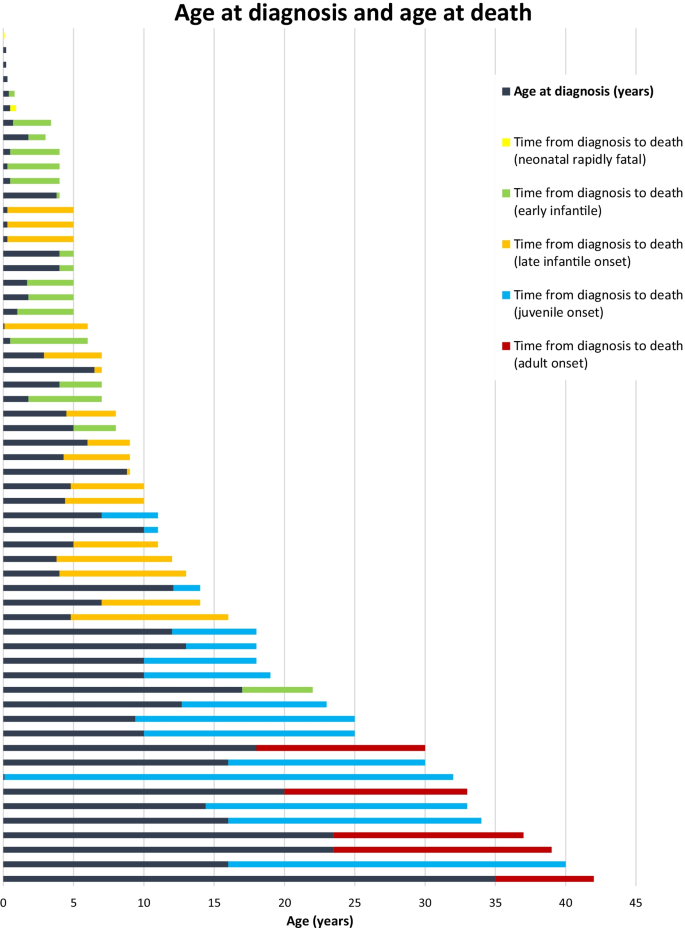
Clinical disease characteristics of patients with Niemann-Pick Disease Type C: findings from the International Niemann-Pick Disease Registry (INPDR), Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
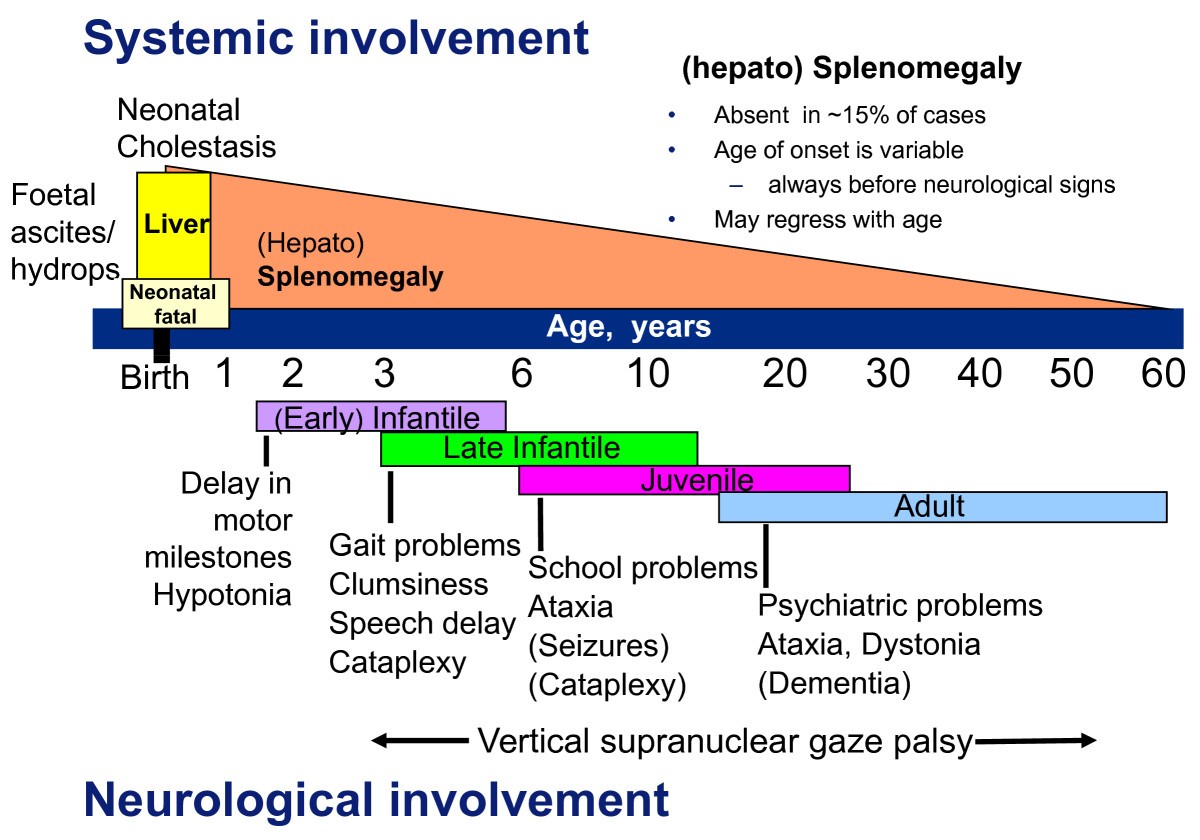
Niemann-Pick disease type C, Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases

Rapid Diagnosis of 83 Patients with Niemann Pick Type C Disease and Related Cholesterol Transport Disorders by Cholestantriol Screening - eBioMedicine

PDF] Niemann-Pick Disease Type C, A Rare Cause of Pancytopenia: A Case Report
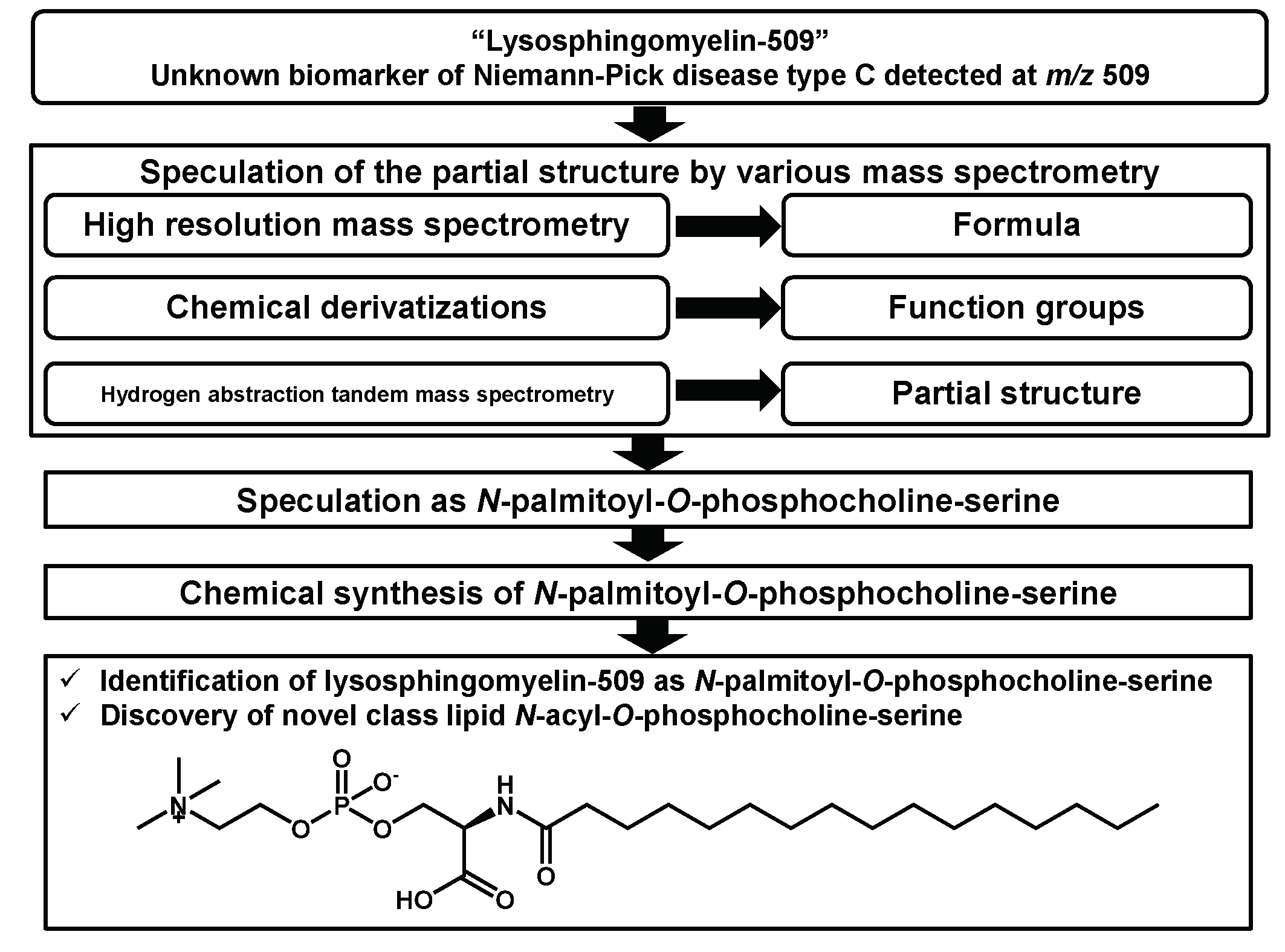
IJMS, Free Full-Text
Consensus clinical management guidelines for Niemann-Pick disease type C - UCL Discovery
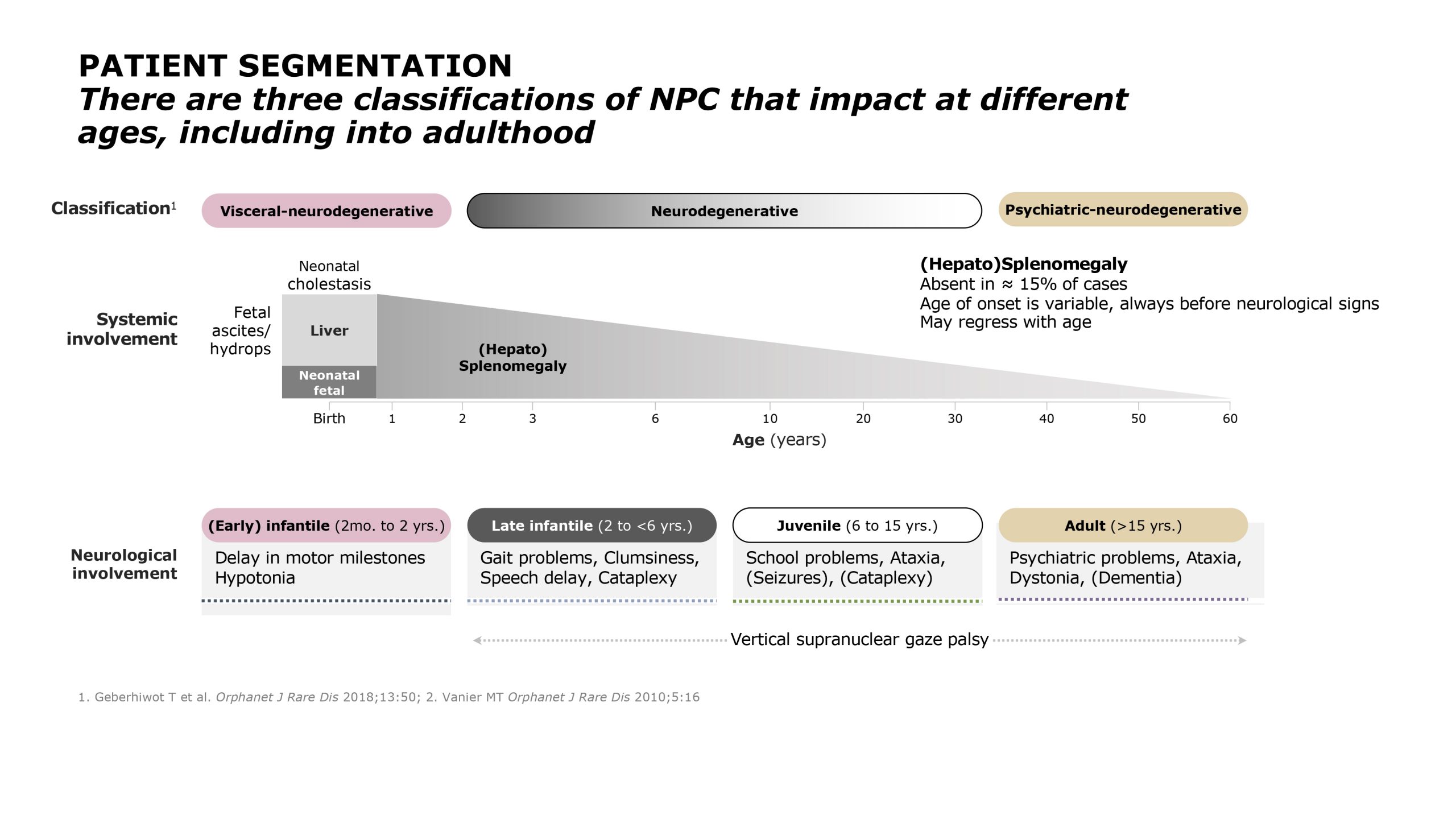
Niemann–Pick Disease Type C
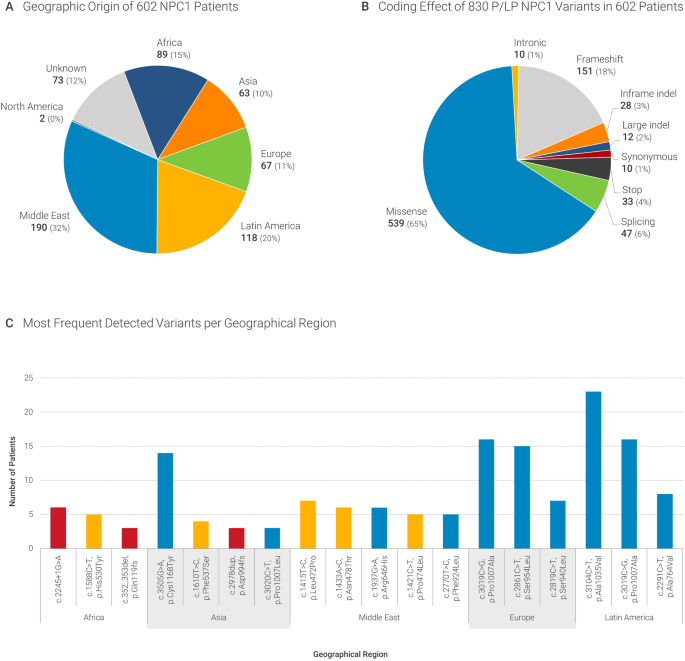
At a glance: the largest Niemann-Pick type C1 cohort with 602 patients diagnosed over 15 years
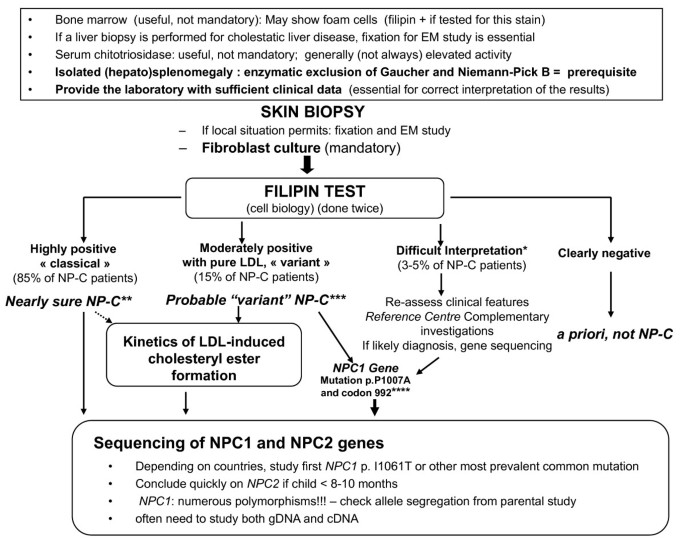
Niemann-Pick disease type C, Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)